
Engineer at a tech services company with 51-200 employees
Some insights into PaaS market
Platform as a Service is a one of the GROWING sector of cloud computing. PaaS basically help developer to speed the development of app, saving money and most important innovating their applications and business instead of setting up configurations and managing things like servers and databases.
Other features buying to use PaaS is the application deployment process such as agility, High Availability, Monitoring, Scale / Descale, limited need for expertise, easy deployment, and reduced cost and development time.
Major forces driving the PaaS
- Pay as you Go
- Low start up cost
- Leave the plumbing to expert
- PaaS handles auto scaling/descaling, Load blancing, disaster recovery
- PaaS manages all security requirements
- PaaS manages reliability, High Availability
- Paas manages manay third party addon’s for you
Barrier to PaaS adoption?
- Less Control over Server and databases
- Have to be expert to mange security controls and audits
- Costs will be very high if not governed properly
- Premature and dobious in current day and age
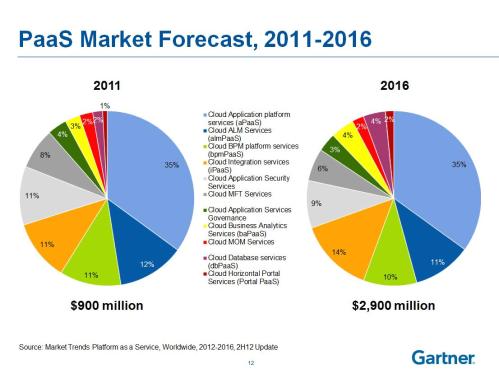
Major PaaS providers are Heroku, Jelastic, and Engine Yard. When we talk about revenue, The global PaaS market is estimated to grow from $1.28 billion in 2013 to $6.94 billion in 2018 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.54% in this period. In terms of geographies, North America continues to be the biggest market for PaaS solutions. In 2012, PaaS revenues ($1.2 billion) was the tenth of the size of SaaS ($14.4 billion), a fifth of IaaS ($6.2 billion), and just a tiny fraction of BPaaS ($84.1 billion).
PaaS has always taken a very small space in the cloud computing arena as compared to the other two segments: IaaS and SaaS. But the trend has recently shown a drift with PaaS market showing a very high growth rate in terms of revenue. Though it is still not as huge as the other two segments but now holds a significant proportion of the pie. PaaS has now been adopted by most of the big cloud computing and IT solution providers like Amazon, IBM, Google etc. as one of their main services.. Many small players have also emerged and made the market very dynamic and competitive. Application developers are benefiting from this fact resulting in more adoption and thus increasing the demand for PaaS all the more in various sectors.
We expect to see more and more application development companies choosing PaaS over IaaS or traditional Hosting, as they can then focus on driving innovation and building apps that change their interactions with customers, partners and community. It will make them free of the details of infrastructure, so they can push the possibilities of the latest technology to build great web and mobile applications.
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
Engineer at a tech vendor with 51-200 employees
All That Cloud: Amazon, Google App Engine, Windows Azure, Heroku, Jelastic
You wanna be in the cloud? You have plenty of options. I’ve evaluated or used many of them, so here are a few words about each. (I will include some Java-related comments, as I’m using Java, but most of the things apply to all (supported) languages). But before I go into a bit more details for each service, let me summarize what “the cloud” actually means when it comes to hosting your applications:
- auto-scaling – if there is an increased demand, you automatically get more resources (more virtual machines in most cases) to handle the requests. For the regular application this is rarely useful, but it’s nice to have it and be sure that your service never dies because the load is too high
- pay what you use – simply put, this is in fact the option to choose small servers when you are small, and bigger servers when you are big. The “cloudy” thing here is that you can do that easily, rather than reconfiguring some remote machines
- cloud infrastructure – this is fancy talk for “we deploy these services and take care that they are working”. So instead of installing and configuring a message queue on your machines, you hook up to an already installed and managed message queue. Or database, email service, or cache.
- management tools – you get consoles, command-line tools and web UIs for handling your installations. This is both a plus (the tools are higher level than working with native commands), and a minus (there’s a learning curve)
- load balancers – all services offer these, and you rarely care what’s the software and hardware of the load balancer
The overall plus is the ease of use – you need way less system administration knowledge, and even if you have it, you need to do much less in order to have a real-world-ready application. It is not necessarily cheaper than regular servers (actually, it might be more expensive). But let’s see what each service does:
Amazon Web Services (AWS). This is the most popular option.
- General flow: you create an EC2 instance, which is a virtual machines, ssh to it and have full control. You can bring up and kill copies of your instance whenever there’s higher load.
- Flexibility: since you have root control over your machine, it is very flexible.
- Usability: the AWS console and the Elastic Beanstalk give you very nice UI for managing applications. With Beanstalk you can deploy applications without even opening a console, just drop a war file. In reality you will at least need to provide some configuration though. The best thing is having predefined instance images, so you can have “Tomcat with MySQL” up and running within a minute. There are already nice solutions built ontop of the Amazon API, like RightScale.
- Features: in addition to the basic instance functionality, you have a lot of extras – managed database, elastic IPs, DNS, cloud storage, CDN, mail service, message queue, cache (this one is not that good, btw), etc. So instead of installing and managing these services on your instances, you can use the Amazon versions.
- Pricing – you are charged for the number of hours your instances are running
- Trial: yes, 1 year (a micro instance).
Google App Engine (GAE). This is a PaaS (Platform as a Service), so you don’t get your own virtual machines and are limited in the use of some standard APIs (for example, you can’t spawn threads), and you can’t use a file system (you need the Blobstore API instead)
- General flow: you create an application and deploy it (through command line or IDE plugin). You don’t manage servers and you don’t have ssh – you have just the app. The app runs in a sandbox, and you may need to use some proprietary APIs in order to store to a NoSQL store, use MapReduce, etc. You have less control. You can browse the datastore, view log files and performance metrics via the admin UI, as you don’t have regular access to the target “machine”
- Flexibility: low – you deploy to a sandbox. You are limited to the configurations the admin UI offers you
- Usability: the admin UI is OK (not perfect, but I can’t say something bad)
- Features: fewer extras, but still good ones – email, datastore, task queue, memcached, etc.
- Pricing – generally, you are charged for the amount of resources you are consuming
- Trial: yes, its is free as long as you use small amount of resources
Windows Azure. You get virtual machines, you can use remote desktop / ssh to administer them.
- General flow: you create a virtual machine and that’s it (similar to AWS). You can also deploy simple web sites using php, asp or node.js (which is PaaS, similar to GAE)
- Flexibility: high for the VM, low for the PaaS
- Usability: the admin UI is OK
- Features: caching, database, service bus
- Pricing – fine-grained, pay-as-you-go or prepaid plans
- Trial: yes, 2 months (the smallest virtual machine)
Heroku. Platform as a Service – you deploy an app in a sandbox and have a lot of useful add-ons for other services. You have two types of “dyno” – one that services web requests, and one that services background requests.
- General flow: you download the heroku toolbelt, run it (the latest version fails on Windows though – it installs ruby 1.9.2 and requires 1.9.3, so you have to edit the bat file) and then use it to create and deploy applications
- Flexibility: low, because you run in a sandbox, but each add-on is configurable and there are a lot of add-ons, so it’s better than other PaaS options. The bad news for Java developers is that it only supports deployment by checking out from git, and building with maven. No other version control system or build tool. (there is hg-git adapter, which you can try if using mercurial, but it starts getting hacky)
- Usability: there is a need for command-line work, which is not that usable. The web UI is OK.
- Features: most of the things you can imagine are available as add-ons
- Pricing – you pay per dyno, per database and per add-on (if paid)
- Trial: yes, you get 750 hours monthly for free – this means you get it for free if you have low usage
Jelastic. Platform as a Service for Java only – you deploy an app in a sandbox. You can configure the architecture and use various 3rd party services. It’s not as popular as the other services, but I got an app running quickly (with some useful input from their support)
- General flow: you create an application, choose an architecture via a nice UI (it’s reconfigurable later), and then deploy your war file. You configure the maximum number of servers that you want your application to use. Everything is configured with the web UI
- Flexibility: low, because you can’t ssh to the machine. However, you are free to edit some application server configurations and have a limited, but sufficient access to the file system, you also can configure each of the additional services you use (databases, for example)
- Usability: the interface is pretty good (I’d say better than the rest)
- Features: you can use additional services – MySQL, MongoDB, CouchDB, memcached, building with maven. (The list is way smaller than what Heroku offers)
- Pricing – you pay per application server instance and per additional service (MySQL, SSL, load balancer, etc.)
- Trial: yes but just 2 weeks
There are many other options, notable RackSpace, which is a traditional hosting company, and the cloud options are simply virtual machines with some “cloudy” features, like auto-scaling. I listed only the popular options that I’ve actually tried (I’ve used AWS, GAE extensively, and deployed sample applications on the other three). The evaluation above does not aim to be complete, and I’ve certainly missed some points here and there.
There’s no “winner” – use different options for different scenarios. But it’s good to know what limitations are imposed by each service, and what’s the approach and general mindset. Because, especially with platforms like Heroku and GAE, you need to change the way you think about deployment.
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
it_user232497Americas Cloud Ecosystem & Partnerships at a tech company with 10,001+ employees
Vendor
All... might be useful to update as many of these details are now invalid.
Buyer's Guide
Heroku
January 2026
Learn what your peers think about Heroku. Get advice and tips from experienced pros sharing their opinions. Updated: January 2026.
881,757 professionals have used our research since 2012.
Engineer at a computer software company with 51-200 employees
Easy Postgres Backup/Restore from Heroku with PGBackups and Rake
Most of my projects lately have been deployed on Heroku. They’ve developed a really nice set of tools to get your Rails (and other) apps from a git repo out into the world. They do really smart things regarding database connections to make things easy to push live. If you follow the standard setup, you’ll be running on Postgres hosted at Heroku.
Often, we want to take data that may be out on a live app (staging or production level) and setup a development machine to have that data. For complex data models and complex data setups, this can be the only way to debug issues that may not have been covered by standard unit/integration tests. With PGBackups, a heroku add-on, and a couple small Rake tasks, this is a snap.
Read the rest of this post here:
http://rcode5.wordpress.com/2013/06/30/easy-postgres-backuprestore-from-heroku-with-pgbackups-and-rake/
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
Developer at a tech services company with 51-200 employees
Great Deployment Options - Heroku, Engine Yard and Amazon
Depending on your needs heroku might get you very far, very fast. I like to use it for clients whose biggest hurdle is not the technology, but in rapidly building a product and iterating quickly. If you already know your customer base, your eventual architecture, and how big your app is going to get, you might prefer to jump ahead to engine yard or amazon, but if you are launching a new app and are still in the process of discovery and exploration, you may find heroku is a good place to start. I work with a lot of small startups and prototype apps, and I think heroku is great for that. Its easy to launch an app quickly, engage users, add new features, scale it up and down as needed, lots of plugins to help you along, while keeping your IT costs reasonable.
Now if the app really takes off, in a sustained way (not just a press-release spike), you will have to decide what changes you want to make to the architecture, and if you have outgrown heroku. I think its great to have Heroku, EngineYard, and Amazon as deployment options. They all have great free options, and each of them has their sweet spot.
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
On my opinion, Heroku has two main pros: speed and simplicity. Since I just want to focus on my applications, it's a convenience to have a managed platform that I can quickly push application to. I also like that it offers plugins which further simplify things like mailservers, backups, logging, etc. But, as a con, it is expensive.
Director of IT at a marketing services firm with 51-200 employees
Why I love Heroku
I first used Heroku to deploy and host Facebook apps, and I’m a big fan ever since.
Lately, I’ve been doing development with node.js and since Heroku supports it (wonder if they were first to offer it), it was a no-brainer:
- deployment via command line with git: nice way to enforce best dev practices
- package management with NPM – everything will be fetched and installed for you
- built-in SSL support on *.herokuapp.com subdomains
- easy monitoring: just type ‘heroku logs’
- easy scaling: just type ‘ps:scale web=x’ or ‘ps:scale worker=x’
- support of environment variables: one example – running multiple instances from the same git repo
- pretty good docs and tutorials
- tons of add-ons: you are free to do pretty much anything (I use Mongolab add-on for Mongo hosting)
- affordable!
Nodejitsu is another service focusing on node.js primarily, but I’ve been reluctant to switch because I just like Heroku so much.
It’s also super cool that they support multiple environments via buildpacks, I’d love to look under the hood and find out how they made it work (and here’s a great post describing their polyglot platform in high-level)
In contrast to the one-language-per-career programmer, today’s up-and-coming developers can often utilize many languages effectively. Borrowing a term from linguistics, we can call these versatile new developers “polyglot programmers.”
For the latest Show&Tell demo, I talked about benefits of using Heroku (as one of the PaaS options) for rapid deployment and easy hosting, so here’s the deck.
This week I’m working on a recommendation chart for cloud hosting, so I’ll share that as well soon.
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
Business Development Staff with 51-200 employees
Cloud Service Models - PaaS
Introduction
In my last post, I looked at some of the major IaaS vendors with a view on how they are being adopted. In this blog I want to look at the broad spectrum of the Platform as a Service (PaaS) models and the compelling reasons that make PaaS a strong option for developers and companies to speed up development and slash costs. Current predictions estimate that globally the PaaS market is predicted to reach $22 billion in 2014. As a whole Europe’s cloud activities will gather pace and momentum, creating 3.8 million cloud professionals and jobs by 2020 mainly within the PaaS sector.
So why is PaaS becoming so popular?
To put it succinctly, PaaS allows developers to have the complete tools, operating systems, middleware and programming language to build their applications. Everything is then hosted and stored by the PaaS vendor. PaaS offers the developer a solution that is a complete software development, testing and deployment environment. In addition it has the benefit that the operating system, virtual machines, infrastructure and IDE are hidden and not a concern to the developer. PaaS service models have automatic scalability to allow for increased usage or spikes in activity – therefore making PaaS a really useful way to build high traffic web apps.
Some of the advantages of using PaaS platforms:
- Fast and speedy development environment: You can commission databases or VMs in seconds and quickly build and deploy code. It provides a single code repository and development environment, which is good for multi-location development teams.
- Huge cost savings on development: Due to faster build times which allow applications to get to market faster.
- Easily deployed databases: Which are configured and managed on the PaaS platform with many providers offering either traditional SQL or NoSQL databases
- Elastic scalability
- Easy support and connectivity: To various software or packages (wordpress, drupal, etc)
- Better security: You can leverage the security protocols from the PaaS vendor for your own application benefit
Who are some of the main PaaS Vendors?
| Heroku |
|
| AppHarbour |
|
| Microsoft Windows Azure |
|
| Amazon Web Services |
|
| Cloud Foundry |
|
There are also numerous other major PaaS Vendors with their own offerings such as OpenStack, Longjump, IBM Smartcloud, Redhat Openshift (based on Linux) Google App Engine, Cloudbees and Engine Yard.
From a UK recruitment perspective: What skills do I need to hire to move my IT development unto a PaaS environment?
Architects: Software development specialists with a strong understanding of how to build on a specific PaaS platform, unlike IaaS architects who generally have come from Infrastructure background. Will have a strong coding background on a core programming language like Java or C# but will understand the build and deployment issues that are alligned to the PaaS platform. Currently as of November 2012, UK contract rates for PaaS Architects are £600-£700 per day and permanent salaries of £75-90k.
Database Admins: These will be specialist Database people with a strong understanding of how the database runs on the PaaS platform. For instance Windows Azure SQL DB is configured and set up different than on-premise SQL servers. It isnt necessarily a vast jump for an existing DBA to learn this, but for companies with large or complex databases, a DBA with specific PaaS product knowledge could be invaluable to move. Currently as of November 2012, UK contract rates for PaaS DBAs are £450-£550 per day and permanent salaries of £60-80k.
Developers: There will be a distinct advantage to hiring developers who have previously built and deployed applications using a PaaS platform such as AWS or Azure. Obviously, these PaaS platforms have been designed to be as easy and as quick to build on as possible, but having a few developers with prior platform development will assist large development teams get to grips with the specific idiosyncrasies of the PaaS platform and will enable the incumbent team get skilled up and productive as quickly as possible Currently as of November 2012, UK contract rates for Developers with PaaS experience are £450-£550 per day and permanent salaries of £60-80k
Lastly, in the UK, compared to the US, the skills pool for IT professionals at the current time with genuine commercial skills in cloud and PaaS technologies is very shallow. Companies looking to move to PaaS development environments are struggling to find external skills. As more companies use these technologies the skills market will expand, but the demand for these skills will be even greater and it will become even harder to recruit.
My advice to any CTO or CIO looking to move their IT to a PaaS development stream is: hire your team early before the rest of the industry wakes up and tries to hire the same person you want to! As a candidate in 2012 and 2013 you will have a distinct competitive advantage and demand on your services if you have strong knowledge of these PaaS platforms and can bring this expertise to a new employer.
Next Time: I will look at the last Cloud service model – SaaS and see how the productized market vendors are getting on and how some of the new technologies are innovating the way we use IT. PS – As an additional note since I started researching and writing this blog a few companies have started to offer a Database as a Service offering – DbaaS – which is a form of PaaS but focused predominantly on providing databases hosted in the Cloud. If this is of interest, check out: bit.ly/XdAnvI
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
Developer at a computer software company with 51-200 employees
6 Ways to get More Bang for your Heroku Buck While Making Your Rails Site Super Snappy
We love Heroku. It makes deployment so easy and quick. However, it can start to get pricey when you add additional dynos at $35 each a month.
With a small amount of work, you can get a lot more out of your Heroku hosting whilst drastically improving the performance of your site. You might need to spend a little bit of cash on other services, but a lot less than if you simply moved the dyno slider up a few notches, and the result will be much better scalability.
So how do we max out the performance of our Heroku apps? First we stop using Heroku for things it’s bad at, then we let it do more of what it is good at, running your application code.
1. Offload Assets to S3 and CloudFront using asset_sync
By default a Heroku dyno is responsible for serving all the assets for your site, so every page load will involve multiple requests to the dyno.
The asset_sync gem modifies asset pre-compilation to sync all of your assets to an Amazon S3 bucket from where they are served directly and freeing up your dyno to handle more requests.
If you want to speed things up even more, you can slap Amazon’s Cloudfront CDN in front of your S3 bucket with multiple subdomains. Michel Sikkes has an excellent guide to serving you assets with S3 and cloudfront. Your assets will be served through Cloudfront from multiple subdomains (e.g. assets[0-3].myapp.com), all of which point to the same bucket. Not only will your assets be served through CloudFront’s speedy global CDN, but most will be downloaded in parallel. Browsers make a limited number of concurrent requests per host name (2 for IE, more for other browsers) so using multiple CNAMEs increases the number of concurrent connections, significantly reducing the page load time for users with good connections.
The cost of serving assets from S3, even with CloudFront, is very cheap and scales directly with the amount of data. Compared to adding another Heroku dyno this is great value, and has the added benefit of speeding up overall page loads.
2. Don’t Upload and Process Files with your Web Dynos
If you use something like CarrierWave or Paperclip, by default the uploading and processing of images is done by your dyno. While this is happening your dyno is completely tied up, unable to handle requests from any other user. If one person uploads a 2Mb image on a slow connection everyone else will be locked out for the duration.
To prevent this from happening you need to decouple the upload process from your dyno. The CarrierWave Direct gem does just this. With a bit of client-side magic it uploads files to S3 directly, rather than through the dyno. The images then get resized by background processes using DelayedJob or Resque. This obviously has the downside that you’ll need a worker running, but there are ways to manage these cost-effectively which I’ll talk about next.
Another option, which we’ve used recently, is the awesome Cloudinary service. They provide direct image uploading, on-demand image processing (including face detection, which even seems to work on cats) and a worldwide CDN all in one package. There is a free tier to get you started, and for $39 (slightly more than one Heroku dyno) their Basic plan will be more than enough for many sites. Obviously you could just spend money on another dyno, but that just scales your performance linearly, without really solving the fundamental performance bottleneck.
3. Background Processing the Smart Way with Delayed::Job and HireFire
Background processing with Delayed::Job is a great way of speeding up your web requests. Potentially slow tasks like image processing or sending signup emails can happen outside of the request-response cycle, making it much snappier and freeing up your dyno to handle more requests. The downside is that you need to run a worker dyno at $35/month.
Michael van Rooljen’s HireFire modifies Delayed::Job and Resque to automatically scale the number of worker dynos based on the jobs in the queue. Because Heroku charge by the dyno/second, spinning up 10 workers for one minute costs the same as one worker for ten minutes, so with HireFire you can potentially get things done quicker while paying less than you would if you ran a dedicated worker dyno.
HireFire does have one limitation, it only works for jobs scheduled for immediate execution. If that is an issue Michael has a HireFire service that will monitor your application for you, so jobs scheduled in the future will be run.
4. Offload Complex Search to a Dedicated Provider
If you have an application that needs to perform complex searches over large datasets don’t do it in your application directly. If searches regularly take a long time (a couple of seconds or more) consider using something like Solr (available as a Heroku plugin), Amazon CloudSearch, or one of the many Search as a Service providers. You’ll not only get faster search performance in many cases, but you’ll save vast amounts of development time trying to optimise your in-app search. Of course, if you have a simple application with straight-forward search then this probably won’t be worth it the cost, but it’s something worth considering.
5. Turbo-Charge your Application with Memcache backed View Caching
If you’ve not encountered caching in Rails, stop reading this article right now, go read the Rails Guide to Caching and then DHH’s short guide to key based cache expiry. Caching in Rails 4 will be even better, with improved support for “Russian Doll” caching.
View caching in Rails can have a profound effect on your application’s response time. In the past we have found that rendering pages, especially complex ones with lots of partials, can easily account for two-thirds of the total processing time, much more than you might expect.
Simply using caching will help speed up your application, but the default cache store is not shared between dynos so the benefits are limited. In contrast, a Memcache store is shared between your dynos so they all benefit from any cached item. Heroku has two add-ons that let you very easily add memcache to your project. The Memcachier addon gives you 25mb for free, and is pretty reasonably priced from there on up. Just adding a small cache store of 25mb can make a significant difference to the load time of your pages.
6. Finally: Slice and Dice your Dynos with Unicorn
So after spending a little bit of time, and a relatively small amount of cash, we’ve offloaded much of the work that was being done by our web dyno and onto services that are better suited to it; drastically speeding up our request-response cycle. Our single dyno can now handle significantly more users per minute, who are happier because they get a much faster response from the site.
However the default Heroku dyno configuration only handles one request at a time. If you wanted to increase your level of concurrency in the past you would have to increase the number of dynos. That’s all changed with the release of the Rack server Unicorn which can handle multiple concurrent connections. For most applications a single dyno should be able to handle between two and four connections at a time. The main constraint will be memory (limited to 512mb per dyno), so keep an eye on the gems you are loading in your production environment. Florian at Rails On Fire has done a great introduction on setting up Unicorn on Heroku. If you’ve followed the previous steps you should be using less memory on your web dynos, allowing you to use more threads.
Putting it all Together
At the end of all this we’ve freed up our Heroku dyno from doing things it’s not very good at like serving static files and uploads, and juiced up its performance when doing what it’s great at, serving Rails application requests with no sys-admin in sight.
Each technique can be easily applied to your existing applications, but if you develop with them in mind from the start you get all the benefits with almost no additional work. On their own each one will help the performance of your application, but combining them together will significantly extend the amount of time before you have to start forking out for lots more dynos, and when you do you’ll get much more bang for each of your thirty-five Heroku bucks.
If you’ve got any other tips for getting the most out of a Rails application, whether or not it’s on Heroku, we’d love to hear about it them!
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
Engineer at a tech company with 51-200 employees
How I hosted a local television contest for $2.37 on heroku

Big spender.
There’s my heroku bill after hosting the voting for a local television contest. $2.37. Over 40,000 people used the app over a period of 2 weeks.
I spent the same amount on coffee this morning.
What?! How?!
I’ve always been really interested in scaling and getting the best possible performance out of limited resources.
I had the opportunity recently to build out the voting back-end for a local television contest. Projects like this are fun because I had the flexibility to try out something new and a lot of people would be using it.
The Stack
I wanted to build an API to handle the voting and get the best performance out of it. Usually I’d use Sinatra for this, but this time I chose to try out Goliath, which is a non-blocking Ruby web server for building APIs. I also used Grape since it would make writing the API even easier.
I hosted it on Heroku. My initial goal was to see if I could keep it to only 1 dyno (more fun with a challenge).
If you’re not familiar with Heroku, a dyno is the equivalent of a small virtual server with 512mb of memory. They also give you your first dyno for free. So all I ended up paying for was the postgres basic database add-on.
Stress Test
Before releasing it, I did some stress testing with Siege. I couldn’t have this app failing when it went live.
212.45 transactions per second.
On only 1 heroku dyno.
WOW GOLIATH IS FAST.
Each transaction was a single GET request, that hit the database (postgres) and returned the count of contest votes. Postgres was probably the slowest part of each request. I could optimize even further by caching with memcached. Maybe next time.
The 200+ transactions per second was way more speed than I needed for this app. And much more than I expected to get out of a single dyno.
I knew that the traffic for this app would be pretty sporadic. Highly dependent on when it was mentioned on TV. Without Goliath, I would have needed to use more dynos to account for the spikes in traffic. But with the performance I was seeing out of Goliath, I knew it could handle the peaks with just 1 dyno.
See the details of the Seige test here.
If you’d like to try it out yourself, the app I used to run this contest was a modified version of Mathy Poll. Which is open source and you can grab it on github.
Disclosure: My company does not have a business relationship with this vendor other than being a customer.
This is a really great idea. Thank you for sharing this information with us.
Buyer's Guide
Download our free Heroku Report and get advice and tips from experienced pros
sharing their opinions.
Updated: January 2026
Product Categories
PaaS CloudsPopular Comparisons
Amazon AWS
Microsoft Azure
Red Hat OpenShift
VMware Tanzu Platform
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Google Cloud
Salesforce Platform
SAP Cloud Platform
Pivotal Cloud Foundry
IBM Public Cloud
Google App Engine
Amazon Lightsail
Cloud Foundry
Virtuozzo Application Platform
Render
Buyer's Guide
Download our free Heroku Report and get advice and tips from experienced pros
sharing their opinions.
Quick Links
- Does Heroku charge for support? Do developers need to adopt new technologies?
- Which solution is better: Heroku or Fargate?
- Looking for a cost comparison evaluation for PaaS platforms
- When evaluating a Platform as a Service (PaaS), what aspects do you think are the most important to look out for?
- Pros/cons of Rackspace vs. other leading vendors?
- Cloud Computing: What are the top 3 benefits of public cloud computing in the enterprise?
- What are the main pros and cons of the various PaaS solutions on the market?
- What is the difference between IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS?
- Which platform do you prefer: Azure or AWS?
- If you anticipate needing to scale your application significantly, what is the best solution?















I don't see how the "barriers" are inherent to PaaS:
-->Managing servers is a cost TO BE AVOIDED - so that's actually a benefit of PaaS not a barrier
--> Security is no more difficult than implementing good security practices on a Web App. And much of it is simpler since you don't have to figure out how to optimally configure your Web Server, your Platform server (OS) and your middle ware server for optimal security. you only have to deal with App level and data level security.
-->Costs are inherently LOWER than with VMs since you do not have to have staff managing the VM stack and scaleout is easier to implement so you can start with a smaller instance
--> As for premature.... based on?